Vitamin B12 deficiency and its implications
The functioning of the human body can be compared to the working of a machine. Every day there are numerous processes carried out within our body. For their proper function ‘vitamins’ and ‘minerals’ are extremely important. They constitute the essential nutrients that are vital for our well-being. This is because they each have a specific role to perform and their proper functioning reflects on our overall health. These vitamins and minerals are also known as micronutrients because they are required only in small quantities. Vitamin B12 among others is an important nutrient because it aids in the forming of your DNA and your red blood cells.
How much Vitamin B12 does the body need?
Vitamin B12 does a lot of things for your body but unfortunately, your body doesn’t produce the nutrient or store it. It can only be availed from regular consumption of animal-based foods or supplements. The exact amount of Vitamin B12(measured in micrograms) required on an average varies according to the age of the person
Sources rich in Vitamin B12
Some major sources include dairy products, eggs, fish, meat, and poultry. If you're looking for food fortified with B12, you will have to check the product's Nutrition Facts label.
Results of Vitamin B12 deficiency
A blood test can reveal if you are deficient in Vitamin B12. Another sign that you lack enough B12 may be a swollen, inflamed tongue. Also with age, it becomes harder for the body to absorb this vitamin.
You are more prone to develop vitamin B12 deficiency if
- if your stomach lining has thinned due to Atrophic gastritis
- Pernicious anemia, can make it hard for your body to absorb vitamin B12
- If you have conditions that affect your small intestines, such as Crohn's disease, celiac disease, bacterial growth, or a parasite
- Heavy consumption of alcohol can make it harder for your body to absorb the vitamin
- you have immune system disorders such as Grave’s disease or lupus
- you take medication that interferes with the absorption of Vitamin B12
- A vegan diet can also sometimes lead to Vitamin B12 deficiency
Symptoms of Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Weakness, tiredness, or lightheadedness
- Heart palpitations and shortness of breath
- Pale skin
- A smooth tongue
- Constipation, diarrhea, loss of appetite, or gas
- Nerve problems like numbness or tingling, muscle weakness, and problems walking
- Vision loss
- Problems related to the mind such as depression, memory loss, or behavioral changes
Treatment
If you have a condition like pernicious anemia or have trouble absorbing vitamin B12, you'll need shots of this vitamin. You will require to keep taking these shots, take high doses of a supplement by mouth, or get it nasally. When you don’t eat animal products, you still have options. You can opt for ar diet that includes vitamin B12-fortified grains. You can take a supplement or B12 injections, or a high-dose oral vitamin B12 or a multivitamin that contains B12.
For most people, treatment resolves the problem. But, nerve damage caused by the deficiency can be permanent.

 Appointments
Appointments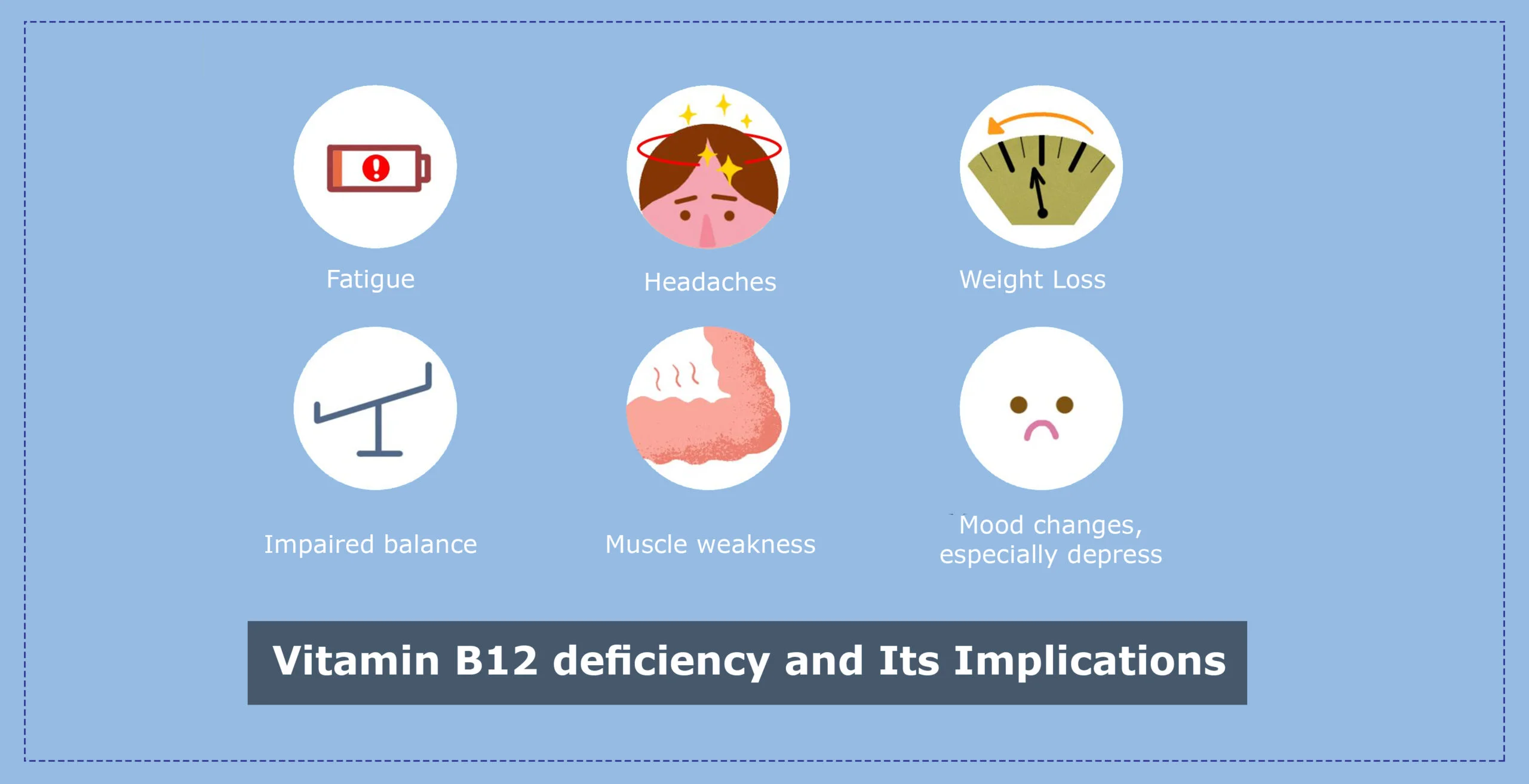




.webp)
_Symptoms,_Causes,_Diagnosis,_Prevention_and_Treatmen.webp)