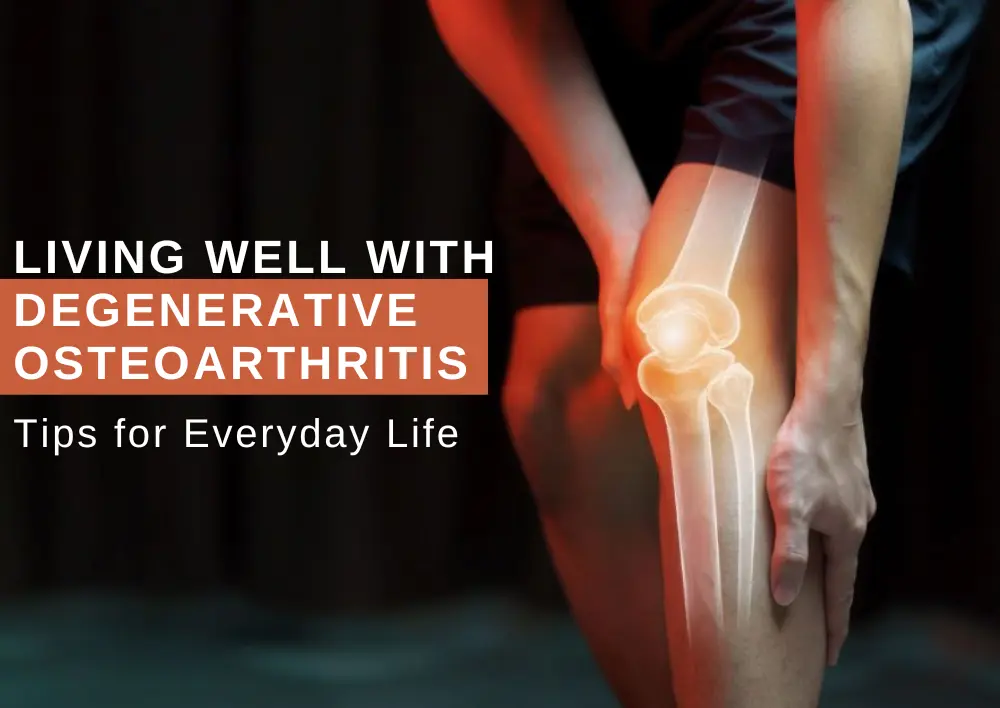
Living Well with Degenerative Osteoarthritis: Tips for Everyday Life
- What is Degenerative Osteoarthritis?
- Indian Statistics on Osteoarthritis
- Types of Degenerative Osteoarthritis
- Symptoms of Degenerative Osteoarthritis
- Why Degenerative Osteoarthritis Occur?
- Osteoarthritis Vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Diagnosis of Degenerative Osteoarthritis
- How is Degenerative Osteoarthritis Treated?
- Tips to Manage Degenerative Osteoarthritis
- Conclusion
Summary
As the body ages, it undergoes several changes, and a common concern is Degenerative Osteoarthritis. It is also known as Osteoarthritis (OA). It is the gradual wear and weakening of joints, affecting millions worldwide and causing pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility. This degenerative joint disease primarily targets cartilage, the protective tissue that cushions the ends of bones in a joint and can also contribute to the development of bone spurs.
Early diagnosis is important to reduce complications and maintain a good quality of life. If you notice any symptoms of osteoarthritis, consult orthopedic specialists. Miracles Apollo Cradle/Spectra, the best hospital for osteoarthritis treatment in Gurgaon, boasts a team of highly experienced orthopedic specialists providing the best treatment for osteoarthritis. Our approach focuses not only on immediate pain relief but also on improving cartilage health.
Continue reading to understand knee arthritis, including its symptoms, causes, treatment, and preventive measures. This article aims to provide valuable information for osteoarthritis patients.
What is Degenerative Osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis (OA) is also known as degenerative joint disease. It is a chronic joint condition characterized by the gradual breakdown of cartilage, the flexible tissue that cushions the ends of bones in a joint. This essential cushioning allows for smooth and pain-free joint movement. However, in the case of OA, this protective cartilage undergoes a degenerative process, leading to several complications.
As the cartilage wears away over time, bones within the joint begin to rub against each other, causing discomfort, pain, and swelling. One of the hallmark features of OA is the reduced flexibility of the affected joint, impacting daily activities and overall mobility.
Indian Statistics on Osteoarthritis
In India, osteoarthritis is a major health concern, affecting a significant portion of the population. Although comprehensive nationwide statistics are challenging to obtain, several studies and surveys provide insights into the prevalence and impact of degenerative osteoarthritis in the country.
-
Prevalence in Urban and Rural Areas: A study published in the Indian Journal of Medical Research reported a higher prevalence of osteoarthritis in urban areas compared to rural areas. This difference may be attributed to lifestyle factors, including sedentary behavior and dietary habits.
-
Age and Gender Distribution: Osteoarthritis in India predominantly affects older adults, with a higher prevalence in women. The risk of developing OA increases with age, and factors such as genetics, obesity, and joint injuries also contribute to its onset.
-
Impact on Workforce and Economy: Osteoarthritis poses a significant economic burden in India due to its impact on the workforce. Individuals with OA may experience limitations in performing their jobs, leading to productivity loss and increased healthcare costs.
-
Challenges in Healthcare Access: Despite the high prevalence of osteoarthritis, there are challenges in healthcare access, particularly in rural areas. Limited awareness, inadequate infrastructure, and a shortage of healthcare professionals contribute to delays in diagnosis and treatment.
Types of Degenerative Osteoarthritis
Degenerative Osteoarthritis (OA) can affect various joints in the body, with different types based on the particular joints involved. Some common types of osteoarthritis include:
1. Knee joint Osteoarthritis:
- It is one of the most common types of osteoarthritis.
- Often occurs due to the wear and tear of the cartilage that cushions the knee joints.
2. Hip Osteoarthritis:
- Affecting the hip joints, this type of osteoarthritis involves the deterioration of cartilage covering the ends of the bones in the hip joint.
-
Can result in pain, stiffness, and reduced mobility in the hip.
3. Hand Osteoarthritis:
- Affects the joints in the fingers and thumbs.
-
Can lead to the formation of bony nodules and joint deformities, causing pain and restricted hand function.
4. Spinal Osteoarthritis:
- Involves the degeneration of joints and discs in the spine.
-
Can lead to spinal stenosis and cause stiffness and back pain.
5. Foot and Ankle Osteoarthritis:
- Affects the joints in the feet and ankles, leading to pain, swelling, and difficulty walking.
-
Can be related to joint deformities, such as bunions.
6. Facet Joint Osteoarthritis:
- Facet joints are small joints present between the vertebrae in the spine.
-
OA of the facet joints can cause stiffness and pain in the back.
Understanding these types of osteoarthritis is crucial for accurate diagnosis and targeted treatment. If you experience symptoms related to any specific joint, consulting with an orthopedist can provide personalized guidance and effective management strategies.
Symptoms of Degenerative Osteoarthritis
The symptoms of osteoarthritis (OA) can vary from individual to individual and depend on the affected joints. Common signs include:
-
Pain: Constant joint pain, especially at the end of the day or following any physical activity.
-
Stiffness: Joint stiffness, particularly in the morning or after periods of inactivity.
-
Swelling: Tenderness and swelling around the affected joint.
-
Decreased Range of Motion: Difficulty moving the joint through its full range of motion.
-
Grinding Sensation: Experiencing a grinding or grating sensation during joint movement.
Why Degenerative Osteoarthritis Occur?
Different factors contribute to the development of degenerative osteoarthritis, including:
-
Age: Osteoarthritis is more common in older adults, as the wear and tear on joints increase over time.
-
Genetics: Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to osteoarthritis, making them more susceptible to the condition.
-
Joint Injuries: Previous joint injuries or trauma, such as fractures or ligament tears, can increase the risk of developing osteoarthritis in the affected joint.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight puts added stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis.
-
Joint Overuse: Repetitive movements and overuse of certain joints in job or sports activities can give rise to the development of osteoarthritis.
Understanding these causes of osteoarthritis is important for both prevention and effective management. If you have concerns about your joint health or fall into high-risk categories, consult with an osteoarthritis doctor near you for personalized guidance and strategies for maintaining joint well-being.
Osteoarthritis Vs Rheumatoid Arthritis
Osteoarthritis (OA) and Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) are two distinct types of arthritis with key differences, despite both affecting joints.
-
Type of Arthritis:
-
Osteoarthritis: Commonly known as "wear-and-tear" arthritis, it affects the cartilage that cushions the ends of bones.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: An autoimmune disease where the immune system attacks the lining of the joints.
-
-
Cause:
-
Osteoarthritis: Occurs due to wear and tear on joints over time, aging, or joint injuries.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the body's immune system mistakenly attacking the joints, causing inflammation.
-
-
Symptoms:
-
Osteoarthritis: Joint pain, stiffness, and reduced flexibility, usually associated with specific joints.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Joint pain, swelling, and stiffness, often affecting joints in a symmetrical pattern.
-
-
Onset:
-
Osteoarthritis: Develops slowly over time and is more common in older adults.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Can develop at any age and tends to have a more prompt start.
-
-
Joint Involvement:
-
Osteoarthritis: Commonly affects weight-bearing joints like knees, hips, and spine, as well as hands.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Often involves smaller joints such as those in the hands and feet but can affect any joint.
-
-
Inflammation:
-
Osteoarthritis: Inflammation is usually mild.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Inflammation is a significant and characteristic feature.
-
-
Morning Stiffness:
-
Osteoarthritis: Stiffness is usually brief, often improving with movement.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Morning stiffness can last for more than an hour and may be a prominent feature.
-
-
Treatment:
-
Osteoarthritis: Management focuses on pain relief, lifestyle changes, and sometimes surgery for severe cases.
-
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Treatment includes medications to suppress the immune system and reduce inflammation.
-
Diagnosis of Degenerative Osteoarthritis
Diagnosing degenerative osteoarthritis (OA) involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies. Here are the key steps in the diagnosis of osteoarthritis:
Medical History:
-
The orthopedic doctor will begin by inquiring about the patient's symptoms, including the duration, location, and nature of joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
-
They may ask about the medical history of joint injuries, family history, or occupational factors.
Physical Examination:
-
The orthopedic specialist will conduct a thorough physical examination to assess joint function, range of motion, and signs of inflammation.
-
They may look for tenderness, joint swelling, or any unusual sounds or sensations during movement.
Blood Tests:
-
Blood tests may be performed to rule out other types of arthritis or medical conditions that can mimic osteoarthritis.
Imaging Studies:
-
X-rays: X-rays are commonly used to view the affected joints, revealing changes in cartilage, bone spurs, and joint space narrowing characteristic of osteoarthritis.
-
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): In some cases, an MRI may be recommended to provide more precise images of soft tissues, such as cartilage and ligaments.
Joint Aspiration:
-
In some cases, joint aspiration may be performed. This procedure involves removing a small sample of synovial fluid from the affected joint with a needle. The fluid can be analyzed for signs of inflammation and to rule out other joint conditions.
How is Degenerative Osteoarthritis Treated?
The treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) aims to manage symptoms, improve joint function, and enhance overall quality of life. Various techniques are employed to relieve pain and discomfort, involving a combination of lifestyle modifications, medications, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions. Here is an overview of common techniques to treat osteoarthritis:
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial, as excess weight can exert additional stress on weight-bearing joints, such as the knees and hips.
-
Medications:
-
Pain Relievers: Your orthopedic specialist may prescribe acetaminophen for managing mild to moderate pain. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen or naproxen, may be recommended to reduce pain and inflammation.
-
Topical Medications: Creams or patches containing NSAIDs or capsaicin may be applied directly to the skin over the affected joint to relieve pain.
-
Nutritional Supplements: Consultation with an orthopedic specialist is essential before using nutritional supplements such as glucosamine and chondroitin sulfate.
-
-
Physiotherapy:
-
Techniques like joint mobilization and manual therapy may be employed to reduce pain and improve range of motion.
-
Physiotherapists design individualized exercise programs focusing on strengthening muscles, enhancing flexibility, and improving joint function.
-
-
Assistive Devices: Supportive devices like braces or splints can help reduce stress on affected joints and improve stability.
-
Injections:
-
Corticosteroid Injections: These provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation when injected directly into the affected joint.
-
Hyaluronic Acid Injections: Used to increase natural joint fluid and improve joint lubrication.
-
-
Surgical Interventions: In severe cases where conservative methods prove ineffective, osteoarthritis surgery may be considered.
-
Joint Replacement Surgery: Involves replacing the damaged cartilage with an artificial one.
-
Arthroscopy: This may be performed for specific joints to remove or repair damaged cartilage.
-
Tips to Manage Degenerative Osteoarthritis
Practical tips for managing osteoarthritis in your everyday life, helping you maintain your well-being and enjoy each day to the fullest.
-
Stay Active: Contrary to popular belief, regular exercise is crucial for managing osteoarthritis. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, or cycling can improve joint flexibility and reduce pain. Work with your orthopedic specialist or a physical therapist to develop a customized exercise plan that suits your needs.
-
Maintain a Healthy Weight: Excess weight puts additional stress on your joints, especially in weight-bearing areas like the knees and hips. By maintaining a healthy weight, you can reduce pain, relieve joint pressure, and improve overall joint function. Consult with an orthopedic doctor to design a personalized nutrition and exercise plan.
-
Protect Your Joints: Take steps to protect your joints during daily activities. Use assistive devices like braces or canes if recommended by your orthopedic doctor. While lifting or carrying items, distribute the weight evenly and use proper body mechanics to minimize strain on your joints. Consider using specific ergonomic techniques, such as maintaining good posture during tasks, to reduce joint stress.
-
Prioritize Rest: Balancing activity with adequate rest is important for managing osteoarthritis. Listen to the body and take breaks when required. Ensure you get enough sleep at night to promote healing and reduce inflammation. Use different relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing or meditation, to manage stress.
-
Warm Up Before Exercise: Before engaging in any physical activity, warm up your muscles and joints to increase blood flow and flexibility. Gentle stretching and range-of-motion exercises can help prepare your body for movement and reduce the risk of injury. Cooling down after exercise is equally important to promote joint comfort and prevent stiffness.
-
Choose Joint-Friendly Foods: Certain foods can support joint health and reduce inflammation. Eat a balanced diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids and anti-inflammatory foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
-
Stay Hydrated: Water helps lubricate joints and maintain the elasticity of connective tissues. Proper hydration is important for joint health. Aim to drink an adequate amount of water throughout the day, and limit the consumption of sugary or caffeinated beverages to avoid dehydration.
Conclusion:
Living well with osteoarthritis requires a holistic approach that incorporates regular exercise, a healthy lifestyle, and mindful self-care. By seamlessly integrating these tips into your daily routine, you can effectively manage osteoarthritis symptoms and improve your overall quality of life.
If you are experiencing the symptoms of osteoarthritis, it is crucial to consult with an orthopedic doctor near you. Seeking professional guidance ensures a personalized approach tailored to your specific needs and conditions.
Miracles Healthcare: Your Partner in Arthritis Management
At Miracles Healthcare, our experts provide a range of effective treatment options to manage arthritis. These options encompass pain management therapies, medication, and advanced non-surgical and surgical interventions. Our team of highly experienced osteoarthritis doctors in Gurgaon utilizes advanced techniques to treat patients effectively.
Our hospital facilities include Miracles Apollo Cradle, Miracles Apollo Cradle/Spectra, Miracles Fertility & IVF Clinic, and Miracles Mediclinic. Conveniently located in Sec 14, Sec 56, and Sec 82, our facilities aim to make daily healthcare more accessible for the people of Gurgaon.
If you are seeking personalized advice or considering treatment for degenerative osteoarthritis, Miracles Healthcare is here to support you on your journey to improved joint health.
Frequently Asked Questions
Lifestyle changes, physiotherapy, pain-relieving medications, and joint injections can all be used to manage degenerative osteoarthritis. For severe problem, your doctor may recommend surgery to relieve your pain and improve the mobility.
Pain of degenerative osteoarthritis can range from mild discomfort to severe.
There is no major difference. Degenerative arthritis is simply another name for osteoarthritis. They are caused by the slow wear and tear of joints.
Pain relievers, anti-inflammatory medicines, and topical gels are commonly used. However, the best option depends on the patient’s condition.
Miracles Healthcare is among the best hospitals in Gurgaon, offering expert orthopedic care and advanced treatment for degenerative arthritis.







_Causes,_Symptoms_Effective_Management_Tips.webp)




Was the information useful?
0 0